The Power of AWS VPC - 04/02/2024
AWS VPC components with cli hands on
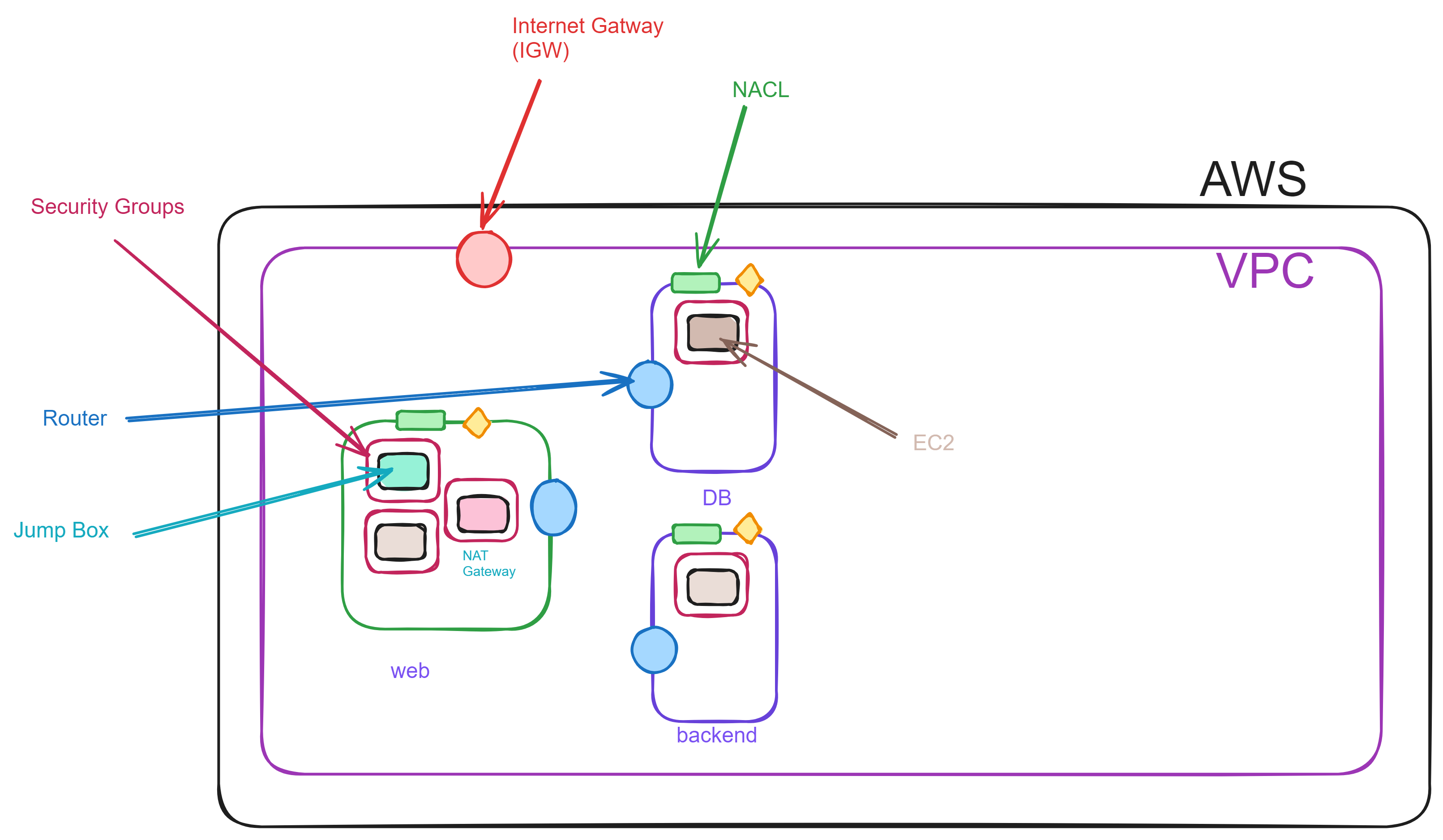
VPC Networking Components :
-
Subnet
-
Internet Gateway
-
Route Table
-
Security Group
-
NACL
-
DHCP Option Set
-
NAT Gateway
-
Egress only Internet Gateway
-
Elastic IP Addresses
-
VPC End Points
-
VPC Peering
Subnet
-
When you create a subnet, you specify the CIDE block for the subnet, which is a subset of the VPC CIDR block.
-
Each subnet must reside entirely within one Availability Zone and cannot span zones.
Internet Gateway
-
An Internet Gateway is a horizontally scaled, redundant and highly available VPC component that allows communication between instances in your VPC and the internet.
-
It is therefore imposes no availability risks or bandwidth constraints on your network traffic.
Route Table
A route table contains a set of rules, called routes, that are used to determine where network traffic is directed.
Security Group
-
A security group acts a s a virtual firewall for your instance to control inbound and outbound traffic.
-
When you launch an instance in a VPC, you can assign up to five security group to the instance.
NACL
A network access control list (ACL) is an optional layer of security for our VPC that acts as a firewall for controlling traffic in and out of one or more subnets.
DHCP Option Set
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) provides a standard for passing configuration information to hosts on a TCP/IP network.
NAT Gateway
You can use a network address translation (NAT) gateway to enable instances in a private subnet to connect to the internet or other AWS services, but prevent the internet from initiating a connection with those instances.
Egress only Internet Gateway
An Egress only Internet Gateway is a horizontally scaled, redundant, and highly available VPC component that allows outbound communication over IPv6 from instances in your VPC to the internet and prevents the internet from initiating an IPv6 connection with your instances.
Elastic IP Addresses
-
An Elastic IP Addresses is a static IPv4 address designed for dynamic cloud computing. An Elastic IP Addresses is associated with your AWS account.
-
With an Elastic IP Addresses, you can mask the failure of an instance or software by rapidly remapping the address to another instance in your account.
VPC End Points
A VPC endpoint enables you to privately connect your VPC to supported AWs services.
VPC endpoint services powered by PrivateLink without requiring an internet gateway, NAT device, VPN connection, or AWS Direct Connect connection.
VPC Peering
-
A VPC peering connection is a networking connection between wo VPCs that enables you to route traffic between them using private eIPv4 addresses or IPv6 addresses.
-
Instances in either VPC can communicate with each other as if they are within the same network.
Lets discuss some of this in more detailed way
Default VPC
-
172.31.0.0/16 CIDR block is assigned to the VPC.
- 65,536 private IPv4 addresses.
-
One subnet (size /20) per Availability Zone is created
-
4096 addresses per subnet
-
5 are reserved by AWS
-
-
Internet gateway is created and attached to the default VPC.
-
Default security group and associate it with your default VPC.
-
Default NACL and associate it with your default VPC.
-
Default DHCP options set for your AWs account with your default VPC.
Security Groups
-
Security Groups are firewall rules that are attached to the network interfaces of the AWS resources.
-
Rules:
-
Inbound Rules
-
Outbound Rule
-
-
SGs are stateful
-
The traffic that is allowed is automatically allowed to go out.
-
up to 5 Security Groups can be assigned to a resources.
-
You can’t add a deny rules
-
All rules are evaluated for the traffic coming in.
-
If a packet does not match any rule, then a a packet is not allowed.
Network ACLs
-
Security features at the subnet level.
-
A NACL can be attached to multiple subnets.
-
A NACL has a numbered list of rules that are evaluated in the ascending order *lowest first)
-
Explicit Allow or Deny
-
Rules:
-
Inbound
-
Outbound
-
-
Once a packet matches a rule. no further rules are processed.
-
NaCL is stateless:
-
You need inbound and outbound rules.
-
This is because the NACLs operate at the OSI layer 4.
-
NAT Gateways
You can use a network address translation (NAT) gateway to enable instances in a private subnet to connect to the internet or other AWS services, but prevent the internet from initiating a connection with those instances.
-
You will need a Public Subnet to put the NAT Gateway in.
-
You will need an Elastic IP address.
-
Update “Route Table” of the private subnet to direct the internet traffic to the NAT gateway.
-
Each NAT gateway is created in a specific Availability Zone and implemented with redundancy in that zone.
NAT Instance
-
Provides NAT service (like NAT Gateway).
-
Managed by customer as an EC2 instance, The performance depends on the size of the EC2 instance.
-
Not Highly Available.
-
Creating NAT instance -> Use Community AMI (search for NAT)
-
NAT instance in placed un the public subnet,
-
Update Route Table of the private subnet to direct the internet traffic to the NAT gateway.
Creating VPC Components Using AWS CLI
Things we are going to made :
VPC
2 or 3 subnets
Internet Gateaway -associate it with one of the subnet to create public subnet
security group
EC 2 instance
SSH to EC2
create a VPC
aws ec2 create-vpc --cidr-block 192.168.0.0/16
copy VpcId from the output of previous command.
ex VpcId: ID = vpc-00d41a71782c5eef
Now create subnet :
aws ec2 create-subnet --vpc-id vpc-[ID] --cidr-block 192.168.0.0/24
and replace ID with 00d41a71782c5eef (something like this)
so , the command will become :
aws ec2 create-subnet --vpc-id vpc-00d41a71782c5eef --cidr-block 192.168.0.0/24
copy the subnetId from the output of the previous command.
Use this command to describe your route table
aws ec2 describe-route-tables --route-table-id rtb-XXXXX
it will look like this : "SubnetId" : "subnet-XXXXXXXXXX"
Now, create another subnet using same command and copy its SubnetId.
Now create internet gateway :
aws ec2 create-internet-gateway
And copy the InternetGatewayId. It is looking something like this "igw-XXXXXXXXXXXX"
Currently our IGW is in detached mode. Now attach it to VPC. For doing that we need vpc id and internet gateway id
aws ec2 aatch-internet-gateway --vpc-id vpc-XXXXXX --internet-gateway-id --igw-XXXXXX
now, create a routing table
aws ec2 create-route-table --vpc-id vpc-XXXXXXXXXXX
Now, you will see 2 routing table in Route Tables section, the first one is the default one, don’t delete that.
copy the RouteTableId from the output. It looks like this rtb-XXXXXXXX
aws ec2 create-route --route-table-id rtb-XXXX --destination0cidr-block 0.0.0.0./0 --gateway-id igw-XXXXXX
You will get two routes, one is local route. (it is maintained by AWS). And other is the route we just created for IGW for connecting it to internet.
Now assoicate this particular route table to desired subnet.
aws ec2 associate-route-table --subnet-id subnet-XXXXX123 --route-table-id rtb-XXXXX
You will get this as output
{
"AssociationId": "rtbassoc-XXXXX"
}
This command associate the route table with subnet and will make subnet-XXXXX123 a public subnet.
Now assign a public ip address to that subnet id.
aws ec2 modify-subnet-attribute --subnet-id subnet-XXXXX123 --map-public-ip-on-launch
Now create a security group :
aws ec2 create-security-group --group-name SG_SSHAccess --description "SSH access" --vpc-id vpc-XXXX
You will get something this like this in output
{
"GroupId": "sg-XXXXX"
}
Copy that GroupId and save it.
Now we will add inbound rules to this security group to allow ssh.
aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress --group-id sg-XXXXX --protocol tcp --port 22 --cidr 0.0.0.0/0
Now create a EC2 instance.
aws ec2 run-instances --image-id ami-XXXXXX --count 1 --instance-type t2.micfro --key-name [your-aws-ssh-key] --security-group-ids sg-XXXXX --subnet-id subnet-XXXX
Copy InstanceId from the output.
Run this command to describe your ec2 instance.
aws ec2 describe-instances --instance-id XXXXXX